How a Simple Process Drives Safety Compliance
Safety management systems have come a long way in the last 250 years. Just think back to workplace conditions during the Industrial Revolution – almost no pay, child labour, very long hours, and extremely dangerous work conditions with exposure to chemicals, accident-prone machinery, and no WHS requirements whatsoever.
But this has changed over the years. Legal reforms and acts were introduced – the Factory Act, the Employer’s Liability Act, and finally, the 1974 Health and Safety at Work Act. This legal document became the foundation for workplace health and safety processes in the UK and the rest of the world. And it led to the increasingly more complex safety processes we have today.
The core purpose of WHS is to keep people safe. Simple. With the increasing complexity of requirements and standards, Business owners, project managers and safety officers alike have to be careful of falling into the trap of using compliance to document requirements like the SWMS as their main measure of WHS compliance. This article looks at why adhering to document requirements is a poor standalone indicator of compliance. We also suggest how a simple safety process drives the success of your WHS compliance.
Documents are Symbols of a Process
Safety isn’t symbolic. It is real and should be treated in the real world, not on a document. Safety management systems do involve documents, but they symbolise a process. For example, a SWMS is a safety planning tool that identifies the risks of high risk construction work and the actions taken to manage those risks. It symbolises the process you are going to take when dealing with the risks and making sure your workplace and its workers are safe from those risks. When it’s under the (judges) hammer, the process symbolised (documented) matters most – not the symbol or the document itself.
Downloading a generic template for your SWMS, JSA, or any other safety document is like taking the symbol without taking the process it represents. And that defeats the whole point of your safety management system and its documents. To comply with WHS requirements, you should be focusing on the processes required to keep your workplace and its workers safe – not just on the documents themselves.
WHS audits look at whether you have followed an effective process that actively reduces the risks in your workplace. They care about if you have actually provided a safe work environment. Not simply whether you have ticked the box of completing a piece of paperwork.
In 2013, The Supreme Court Qld in a case against a QLD construction company for the death of two workers cited:
“work practices focused too much on the work performed onsite and did not pay adequate attention to the dangers presented by the conditions of the site itself”
In other words, not considering risks on the ground, in the real world can have significant impacts when taken to the extremes. Focussing too hard on the details of the tasks to be completed can lead to ignoring all the risks that are actively present
What you focus on matters. And if you want to pass your WHS audit and actually keep your workers safe, then it’s time to focus on the safety management process behind the symbols and documents.
But I still go through a process when filling in a template?
Safety management systems aren’t just about the symbols. They’re about the processes behind them. But you may be wondering – isn’t downloading a generic template still technically a process? Sure. But think about this. What process is more effective at satisfying the Work Health and Safety Act requirement to provide a safe work environment? Is it:
- Find a generic SWMS template on Google, Officeworks or other source
- Complete the boxes provided by the template as best as you can
- Gather up or seek out workers individually and gather signatures
- Store it onsite until the work is done
- Transferring the document to a folder in your office when you are done with the site
Or:
- Identify a the risks onsite, in person
- Build a new SWMS or modify the existing version to cover all task & site-specific risks that are present. Pushed to everyone to sign.
- Monitor how measures are being implemented while work is being completed with real time automated risk rating notifications
- Review by anyone relevant once the work has been completed
- Automatic document storage once complete for any future audits, follow-ups, or learning
From a legal standpoint, the second option is better,
The very purpose of developing a SWMS is to ensure that employers and workers have taken the time to identify the high-risk tasks to be done on site. And then, it is to develop measures to manage these risks and tasks in the context of the work being done. The very nature of a SWMS is that it is specific. It is created specifically in response to a specific site, specific tasks, and specific risks. A generic templated SWMS will not meet the intention behind WHS requirements. Instead, it will defeat the real power of the SWMS and even take away from your safety management.
As WorkSafe Victoria explains, “our concern is not what is written but what actually happens”. A generic SWMS is a symbol of safety that only provides guidance. To focus on the process and comply with WHS requirements, your SWMS and other safety documents need to be customised. It is the second process that is more likely to pass a WHS audit because it demonstrates an active approach to creating a safe work environment. And it is the first process that will get a much more severe punishment when a safety incident does happen, even though both processes are represented by the same type of document.
How to Prioritize the Process
The simplest way to boost the effectiveness of your safety process is to use a digital safety platform like SafeWorkPro. While you can do your safety management physically or digitally, doing it digitally is what will make the difference. Why?
Safety management software simplifies your safety management. Turning a complex process into a simple, easy to understand workflow that allows for an easier way to assess, mitigate, monitor and review workplace risks of all nature. It makes sure that your safety management system is customised, comprehensive, and lets you focus on the process. Leave the document creation, distribution and storage to the software. With safety management software, you can seamlessly customise, prioritise, and ensure your safety management system and its processes exceed WHS regulations.
SafeWorkPro is the Australian safety management software that can make sure your workplace prioritises the process over the symbols.
- Customise your SWMS, JSA, or other safety documents specifically to your worksite using our flexible document builder
- Make sure your specific workplace risks are managed and your workers are safe
- Ensure your company truly complies with WHS requirements
Do all of this seamlessly and in one place with the SafeWorkPro platform. Click the button below to find out more.
More From The SafeWorkPro Blog
What is a Risk Assessment Matrix?
What if I told you that construction risk assessments were so unnecessarily complicated that they actually constrain your productivity? If you’ve ever had to deal with an OHS risk assessment matrix than you’d know what I’m talking about.
Even the best risk assessment matrix can be long and overcomplicated. This means that workers have to stay off the job for longer just to finish the required risk assessment forms. But what is a risk assessment matrix?
Risk Assessment Matrix Template
Risk assessment matrices are a common tool for risk evaluation and are used through a variety of industries and professions. The aim of a risk assessment matrix is to determine the likelihood and consequence of various health and safety hazards and risks. Usually presented in a table or graph format, risk assessment matrices usually offer three standards:
1-2: Low likelihood, low consequence: this area usually indicates that the health risks at work are either effectively controlled or are not prevalent enough to warrant concern.
3: Medium likelihood, medium consequence: these risks are usually judged to be controllable within reason and represent the bare minimum of acceptable risk in the workplace.
4-5: High likelihood, high consequence: risks identified in this area require stronger control measures to fall within reasonably practicable health and safety standards.
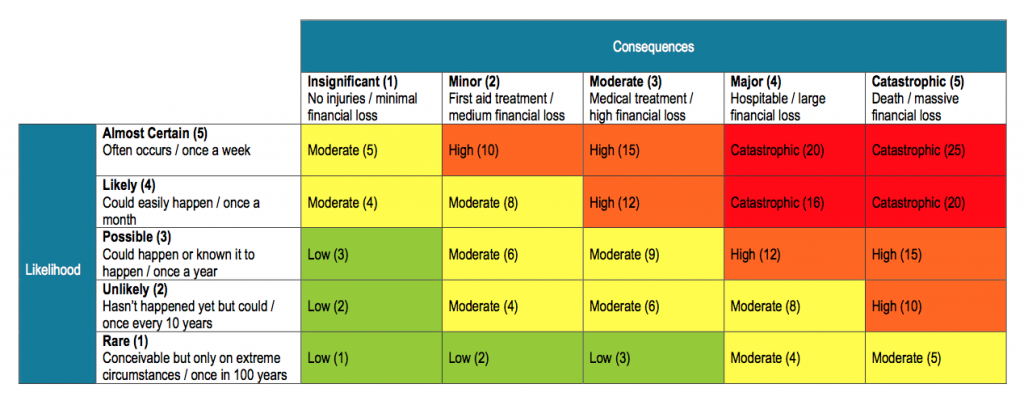
Along each axis of the graph, the various levels of consequence and likelihood are numbered. To retrieve an accurate level of total risk, these numbers are multiplied together according to where the specific risk falls on the graph or table. Although most businesses will have different guides, this general risk assessment template provides a basic understanding of a standard risk assessment matrix example.
Worksafe Australia Codes Of Practice
In Australia, every state or territory has it’s own health & safety regulations enforced by their respective governmental authority. To ensure a safe workplace for all Australians, Safe Work Australia develops model codes of practice for a variety of high risk construction work.
The purpose of these safety policies is to harmonise safe working practices and procedures under one legal framework. Although each state or territory has its own regulator for the enforcement of safety laws in the workplace, Safe Work Australia’s codes of practice outlines the health and safety standards required under the WHS Act. These practical guides only become enforceable after the government of each state or territory approves them. Approved codes of practice are also admissible in court meaning if legal proceedings were to occur, the code of practice can be used as evidence as to what is know about a hazard, risk or control measure. The codes of practice will in turn be used as a reference point to determine what is reasonably practicable in the relevant situation.
There are currently 32 model codes of practice published by Safe Work Australia ranging from asbestos handling to confined spaces. More details of the codes can be found at Safe Work Australia’s website.

Safety Tips In The Workplace
The beauty of Safe Work Australia Month is that it not only increases the public’s awareness of safe working practices but it also fosters the sharing of innovative ideas. This approach gives employees and employers the ability to form occupational health and safety procedures that evolve with safety laws in the workplace. In one Safe Work Month […]





